Latent and sensible cooling loads to consider in design of HVAC systems
The design cooling load (or heat gain) is the amount of heat energy to be removed from a house by the HVAC equipment to maintain the house at indoor design temperature when worst case outdoor design temperature is being experienced. There are two types of cooling loads:
- sensible cooling load
- latent cooling load
The sensible cooling load refers to the dry bulb temperature of the building and the latent cooling load refers to the wet bulb temperature of the building. In the summer, humidity influence in the selection of the HVAC equipment and the latent load as well as the sensible load must be calculated.
Factors that influence to the sensible cooling load
- Glass windows or doors
- Sunlight striking windows, skylights, or glass doors and heating the room
- Exterior walls
- Partitions (that separate spaces of different temperatures)
- Ceilings under an attic
- Roofs
- Floors over an open crawl space
- Air infiltration through cracks in the building, doors, and windows
- People in the building
- Equipment and appliances operated in the summer
- Lights
Notice that below grade walls, below grade floors, and floors on concrete slabs do not increase the cooling load on the structure and are therefore ignored.
Other sensible heat gains are taken care of by the HVAC equipment before the air reaches the rooms (system gains). Two items that require additional sensible cooling capacity from the HVAC equipment are:
Other sensible heat gains are taken care of by the HVAC equipment before the air reaches the rooms (system gains). Two items that require additional sensible cooling capacity from the HVAC equipment are:
- Ductwork located in an unconditioned space
- Ventilation air (air that is mechanically introduced into the building)
Sensible Heat Load and Required Air Volume Chart
Sensible heat load - heating or cooling - and required air volume to keep temperature constant at various temperature differences between entering air and room air are indicated in the chart below:
Factors that influence to the latent cooling load
Moisture is introduced into a structure through:
- People
- Equipment and appliances
- Air infiltration through cracks in the building, doors, and windows
Other latent heat gain is taken care of by the HVAC equipment before the air reaches the rooms (system gain).
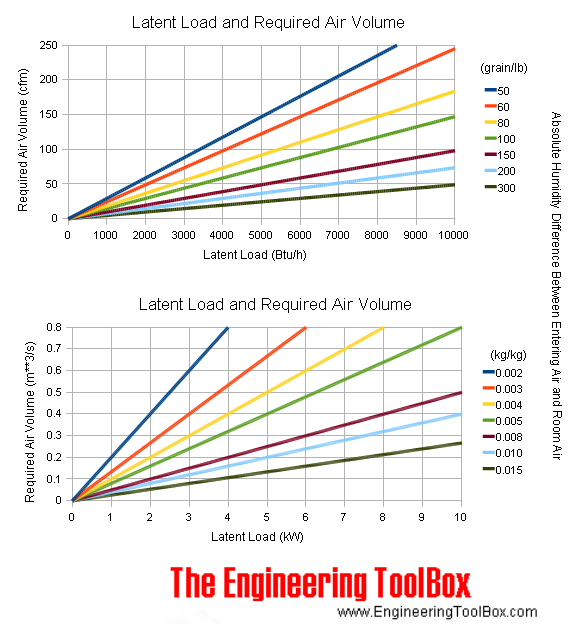
Latent Heat Load and Required Air Volume Chart
Latent heat load - humidifying and dehumidifying - and required air volume to keep temperature constant at various temperature differences between entering air and room air are indicated in the chart below:

No comments:
Post a Comment